If you haven't had the experience of suffering through an incompetent, insecure, or plain old bully of a boss, consider yourself lucky! According to a Gallup study, companies fill management positions with ineffective leaders more than 80% of the time. The odds are high that most of us have a very personal "horrible boss" story.
Gallup has studied performance at hundreds of companies and measured the engagement of 27 million employees and more than 2.5 million work units over the past two decades. More than half of American employees have left their jobs because of a bad manager. Sadly, that means that there is no shortage of bad bosses.
Bad bosses (a.k.a. "ineffective leaders") don't just suck the joy right out of work, they damage company culture, and decrease employee engagement, creativity, innovation, and productivity as well as undermine collaboration and team performance. The way leaders handle organizational challenges set the tone for the level of psychological safety employees feel to raise concerns, ask questions or challenge the status quo.
The Great Resignation is illuminating what employees want and need from their leaders to thrive at work.
Spoiler Alert: it's not that complicated and it's not new.
A 2022 Pew Research Center survey discovered that the lack of opportunities for advancement and feeling disrespected at work are among the top reasons Americans quit their jobs last year. A decade-long study published in 2021 involving more than 100,000 participants in 26 countries including all major job titles across all major industries identifies the eight attributes that employees value most in managers with support and consideration at the top of the list.

Source: Employee Experience Gap. Engage2Excel. 2021
Imagine sitting in a team meeting and your boss invites your team to ask for help if you need it. You know the line, "We're here to support you; don't hesitate to let us know if you need anything." So, you raise your hand and admit that you're struggling to complete a project because you don't have the necessary information. (After all, you were just invited to ask for help.) Now imagine, your boss demeans you with a comment about your inability to complete your work rather than acknowledge the information gap and get you what you need so you can complete your work -- in front of the team. How many other people do you think are going to ask for help?
Support? No.
Consideration? Nope.
Dignity? Hardly.
Respect? Not even a little bit.
Being disrespected is far more damaging that many people realize. We internalize and feel being rejected, marginalized and unsupported much more intensely than any comments of praise. And when we are disrespected in front of peers, have a micromanaging boss or feel excluded from decisions that impact job performance, we experience the added pain of threat to social status. The body's responses to social threats are biochemically the same as its responses to physical threats.
Why do perceived negative comments stick with us so much longer than positive ones? The answer is neurochemistry. Negative feelings like rejection, fear, minimization, and criticism engage the fear/threat center and the amygdala orders up a blast of cortisol which creates an immediate "shut down" of our prefrontal cortex— our "executive brain" that enables strategic thinking, decision making, connectivity with others, creativity, and most of all, trust.This effect can last longer than 24 hours which magnifies the experience and imprints it into memory. The longer we stress over something, the greater the impact.
When we feel dismissed and unsupported, problems become barriers. But, when we feel valued and respected, we are able to embrace problems as challenges we are motivated to solve.
Positive conversations generate a chemical reaction, too. The positive feelings we experience when we feel like we’re contributing members of a team, that what we do is important, and that we can trust people around us produce the neurotransmitter oxytocin - the chemical that elevates our ability to communicate, collaborate, and connect with others. Unlike cortisol, oxytocin activates neural activity in the prefrontal cortex.
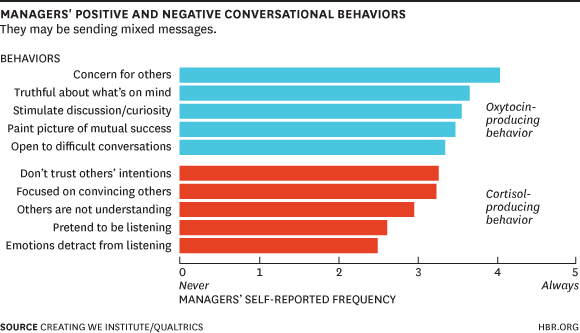
Neurochemistry of conversations has huge  implications in the success or failure of team dynamics. In a recent survey, managers were asked how often they engaged in various positive and negative behaviors. The results were doubled-edged. While most of those surveyed said they demonstrated all five oxytocin-producing behaviors, all five also admitted to all five of the cortisol-producing behaviors. When leaders demonstrate conflicting behaviors, it creates a sense of uncertainty among team members that – you guessed it – generates cortisol.
implications in the success or failure of team dynamics. In a recent survey, managers were asked how often they engaged in various positive and negative behaviors. The results were doubled-edged. While most of those surveyed said they demonstrated all five oxytocin-producing behaviors, all five also admitted to all five of the cortisol-producing behaviors. When leaders demonstrate conflicting behaviors, it creates a sense of uncertainty among team members that – you guessed it – generates cortisol.
What's worse than poor communication? NO communication! Studies show that ignoring employees' work, needs, or questions is almost as bad as shredding their work right before their eyes! Leaders who fail to address problems or obstacles within the organization, ignore requests for help, or neglect to provide feedback or direction send very powerful messages to the team members:
You're not important.
Your work is not important.
Your needs are not important.
You're not worth my time.
It's hard to imagine actually saying those things out loud. Sadly, poor leaders communicate those negative messages all the time in very common everyday behaviors. And from an organizational standpoint, the highly motivated, passionate people are the ones who will leave first because they are motivated by contribution and achievement, and they are confident in their own abilities enough to know they will be valued elsewhere.
The Bottom Line
One thing that has become very clear from the workplace studies over the last decade and specifically the Great Resignation: The real reasons for turnover usually point squarely at leadership. Leaders can cripple organizational culture, but bad bosses kill more than culture. Bad bosses damage the morale, motivation, and productivity of their teams, create unnecessary stress that undermines creativity and innovation, and all of that eventually makes it way to the product or customer which deteriorates the organization's deliverables and reputation. Ultimately, bad bosses send their top talent packing - all based on their actions or inaction.
To learn more about the powerful influence of common ineffective leadership behaviors on company culture in the virtual workplace, check out my e-book: